Medical Tourism Blog
Water Retention Solutions in Korea: Diet IV Therapy and Diet Pills for Effective Relief

Table of contents
- "Diet IV Therapy": A Detailed Look
- "Diet Pills": A Comprehensive Overview
- Best Clinics in Korea for Water Retention
- Seeking "Diet IV Therapy" and "Diet Pills" in South Korea: A Medical Tourist's Guide
- Patient Experiences and Effectiveness: What the Data Shows
- Recommendations for Patients: Making Informed Health Decisions
- References
Water retention, often described as a "swollen body," is a common issue where the body holds onto too much fluid, causing puffiness and swelling. Medically, this is known as edema, which refers to swelling from fluid buildup in tissues. Other terms you might hear include fluid overload or hypervolemia. Since our bodies are made up of 50-60% fluid, any disruption in this balance—especially an excess—can lead to health problems.
Swelling from water retention can show up in the feet, legs, hands, or face. A classic sign is pitting edema, where pressing on the swollen area leaves a temporary dent. Other signs include rapid weight gain (sometimes 8-15 pounds before swelling is obvious), high blood pressure, shortness of breath (especially if fluid reaches the lungs), headaches, bloating, abdominal cramps, and even chest pain if fluid builds up in the lungs (pulmonary edema).
There are many causes for water retention. Diet is a big one—eating too much sodium makes the kidneys hold onto more fluid. Sitting or standing for long periods can cause fluid to pool in the legs and feet. Some medications, like blood pressure drugs, NSAIDs (like ibuprofen), antidepressants, and chemotherapy, can also cause water retention.
More serious causes include heart failure (where the heart can’t pump blood well, leading to fluid buildup), kidney disease or failure (which affects the body’s ability to manage salt and water), and liver cirrhosis (scarring of the liver that leads to fluid in the abdomen). Venous insufficiency (faulty leg veins), deep vein thrombosis (DVT) (a blood clot in the leg), preeclampsia in pregnancy, malnutrition, certain cancers, and lymphedema (often after cancer treatment) can also be to blame.
It’s important to remember that "swollen body" is a symptom, not a disease. Because the causes range from diet to life-threatening illnesses like heart or kidney failure, self-diagnosis or self-treatment is risky. If you notice swelling, it’s crucial to see a healthcare professional to find and treat the underlying cause.
When it comes to "Diet IV therapy" as a solution for water retention, there’s a major problem. Water retention means you already have too much fluid, while IV therapy adds more fluid. This contradiction can be dangerous, especially for people with heart or kidney issues—the very people most at risk for water retention. Giving extra fluids in these cases can make things much worse, so using "Diet IV therapy" for water retention without a doctor’s guidance is not only inappropriate but potentially harmful.
Table 1: Common Pseudonyms for Water Retention
| Common Term | Medical Term |
|---|---|
| Swollen Body | Edema |
| Puffiness | Fluid Overload |
| Swelling | Hypervolemia |
"Diet IV Therapy": A Detailed Look

IV therapy involves injecting fluids directly into your veins. Medically, it’s used to treat dehydration or fix electrolyte imbalances. There are two main types: crystalloid solutions (like Normal Saline, D5W, Lactated Ringer’s) that move easily into tissues, and colloids (like albumin) that stay in the blood vessels. IVs can also deliver medications or nutrients.
The process is precise: a healthcare provider chooses the right fluid, amount, and speed, then inserts a needle into a vein (usually in the arm or hand), connects it to a fluid bag, and monitors the infusion.
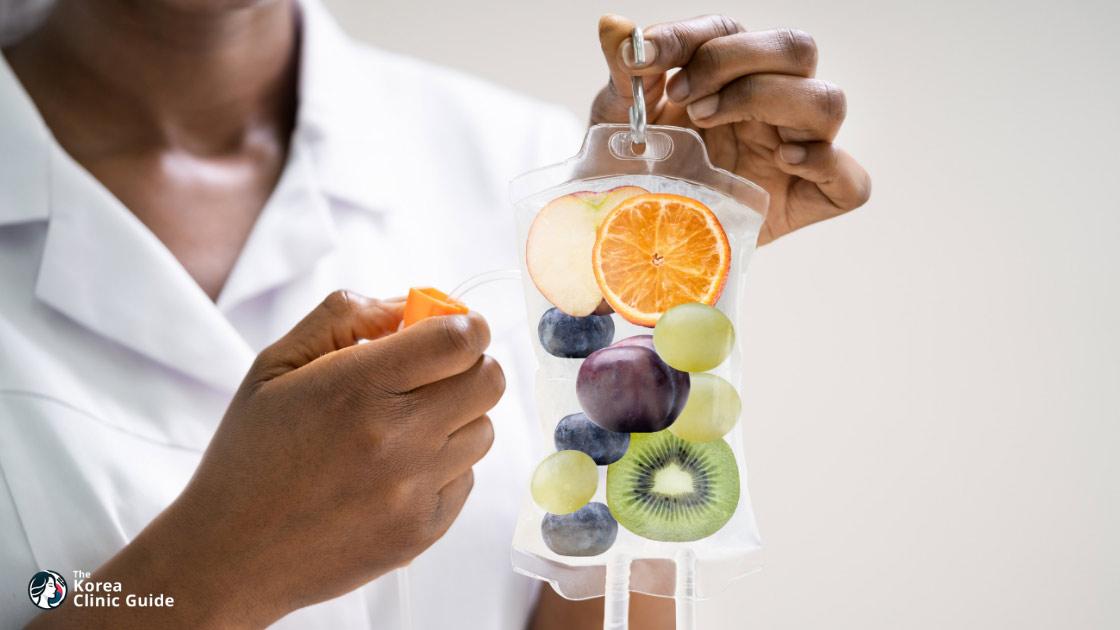
Recently, IV nutrition therapy has become trendy in wellness and beauty circles, marketed as "Diet IV therapy." These are promoted for boosting energy, hydration, immunity, stress relief, and even for "beauty" purposes—think "Cinderella drips," "Celebrity Glow Drips," and more. Some clinics even claim it helps with "post-vacation weight," which is often just temporary water retention. The idea is that IV delivery is faster and more effective than taking nutrients by mouth.
But the science doesn’t back up these claims. No IV therapies are FDA-approved for weight loss, and major medical organizations don’t recommend them for this purpose. Most benefits are anecdotal and likely due to the placebo effect. Studies show that people who get just saline (salt water) report feeling just as good as those who get vitamin IVs. A 2021 South Korean study advised caution, citing a lack of evidence and potential risks. While IV fluids can help if you’re dehydrated, they’re not a direct fix for fluid overload. In fact, adding more fluid can make water retention worse, especially if you have heart or kidney problems.
The marketing of "Diet IV therapy" in South Korea, especially for wellness or beauty, can be misleading. Prices vary widely, with "beauty" or "anti-aging" drips costing much more than basic nutrient drips—often reflecting branding rather than medical value. For those seeking real medical solutions for water retention, this commercial approach is problematic and potentially deceptive.
A major risk of "Diet IV therapy" for people with water retention is "overhydration" and "electrolyte imbalances." Adding fluids can worsen swelling, raise blood pressure, and cause breathing problems. Extra electrolytes can lead to irregular heartbeats, muscle weakness, or seizures. These risks are highest for people with heart or kidney disease, who are already prone to fluid overload. That’s why a thorough medical evaluation is essential before considering IV therapy for swelling.
Table 2: Potential Risks and Side Effects of Diet IV Therapy
| Risk Category | Specific Risks | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|
| Systemic Risks | Overhydration (confusion, headaches, nausea, vomiting, high blood pressure, trouble breathing), Electrolyte Imbalances (irregular heartbeat, muscle weakness, seizures), Vitamin Overdose (oxalate kidney stones, stomach issues), Blood Infection/Sepsis, Medication Interactions, Air Embolism (rare, potentially fatal), Life-threatening adverse effects from certain prescription drugs (e.g., ketorolac, lidocaine) | Heart disease, Kidney problems |
| Site-Specific Complications | Blood Clots, Collapsed Vein, Hematoma (bruising), Infiltration (fluid leaking into tissues), Phlebitis (vein swelling) |
"Diet Pills": A Comprehensive Overview
Diet pills, also called weight loss supplements or anti-obesity medications, are drugs designed to help with weight loss or obesity management. They work in different ways: appetite suppressants (like Phentermine and Lorcaserin) make you feel full faster, fat blockers (like Orlistat) prevent fat absorption, and metabolism boosters (often with caffeine) increase calorie burn. Some are combination drugs that use multiple mechanisms.
Diet pills are usually prescribed for people with a BMI of 30 or higher, or 27+ with health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure. They’re not meant for minor or cosmetic weight loss. In South Korea, prescription is tightly regulated, and a full medical assessment is required before starting. Regular follow-ups are needed to monitor progress and side effects, and these drugs should always be used alongside a healthy diet and exercise.
Despite being marketed as a weight loss solution, diet pills come with serious risks. Side effects can include heart problems (pulmonary hypertension, valvular heart disease, high blood pressure), psychological issues (psychosis, depression, insomnia), and organ damage (liver, gallbladder, or kidney stones). Using diet pills without a proper diagnosis for swelling is inappropriate and can lead to severe reactions, especially since they’re not designed to treat water retention.
The Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) has warned about popular slimming pills. Sibutramine, for example, was restricted in Europe due to heart risks, and Orlistat has been linked to liver damage. A KFDA survey found that 70% of patients taking weight loss drugs experienced side effects like dizziness, thirst, nausea, and depression. Many regained weight after stopping the pills, highlighting their temporary effect.
Importantly, diet pills are not a treatment for "water retention." They target weight loss, not edema. Some, like phentermine, can even cause fluid retention. Using them for swelling without a diagnosis is risky and unlikely to help.
Table 3: Potential Risks and Side Effects of Diet Pills
| Risk Category | Specific Risks | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Heartburn, Gallbladder Disease, Pancreatitis | |
| Cardiovascular | Pulmonary Hypertension (rare, potentially fatal), Valvular Heart Disease (leaky heart valve), Elevated Blood Pressure, Increased Pulse/Heart Rate | Heart disease, High blood pressure, History of stroke |
| Neurological/Psychological | Restlessness, Insomnia, Headache, Dry Mouth, Anorexia, Irritability, Personality Changes, Psychosis (with chronic use), Severe Depression (upon withdrawal) | Epilepsy, Glaucoma |
| Organ Damage | Liver Damage (Orlistat), Kidney Stones (Orlistat) | Severe kidney or liver disease |
| Other | Drug Dependence/Abuse (Amphetamine-like drugs), Dizziness, Excessive Thirst, Runny Nose, Sore Throat | Thyroid problems |
Best Clinics in Korea for Water Retention
Listed below are the best clinics in Korea for water retention:
| Clinic Name | Key Features | Special Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| 365mc Hospital | Leading Korean medical institution for water retention and body contouring; 18 branches; over 5 million cases; expert team of 22 doctors; patient-centered, research-driven approach; comprehensive post-treatment care; exclusive support resources such as meal diary app, seminars, and education. | M.A.I.L. System (motion-capture + AI for surgical precision); LAMS (Local Anesthetic Minimal-Invasive Liposuction); targeted liposuction; Hourglass Hip service; nutrition and diet counseling. |
| Three Wishes Clinic - Myeongdong | Centrally located in Seoul; highly praised by local & international patients; focus on safety, professionalism, patient satisfaction, and the latest technology; individualized treatments; comprehensive skin and body aesthetic services; rejuvenating therapies. | Minimally invasive procedures; specialized treatments for water retention and body aesthetics; botox, fillers, fat-dissolving injections; Shurink, CO2 laser, PDT acne therapy; semi-permanent makeup. |
| 365mc Hospital - Sinsa | Specialized in advanced body contouring; leader in liposuction and water retention treatment; expert and safety-focused medical team; personalized treatment plans for targeted liposuction of various areas; high standards of client satisfaction. | LAMS (Liposuction Assisted Morphological Surgery); minimally invasive targeted liposuction for abdomen, arms, thighs, love handles, and face; advanced body contouring protocols. |
365mc Hospital
365mc Hospital is widely recognized as the leading medical institution in Korea for the treatment of water retention and body contouring. With more than two decades at the forefront of liposuction and obesity care, 365mc merges exceptional clinical expertise with cutting-edge medical technology to offer results-driven, patient-centered solutions. The extensive reach of 18 branches across the country, a distinguished team of 22 main doctors, and an outstanding safety record built on over 5 million cases, position 365mc not only as the largest but also the most trusted clinic for managing body fluids and excess fat. Their approach to water retention is rooted in the understanding that persistent swelling often stems from a combination of localized fat accumulation and lymphatic or circulatory issues, both of which are directly addressed through their advanced treatment repertoire.
Highlights of Why 365mc is Best for Water Retention:
- Over 3000 successful liposuction surgeries and 5 million treatments underscore their unparalleled experience in addressing body fluid imbalances and contouring issues.
- Specialized expertise in body sculpting ensures targeted removal of stubborn fat that can exacerbate water retention, leading to immediate improvement in contour and swelling.
- Exclusive use of the M.A.I.L. System, integrating motion-capture and artificial intelligence, provides superior surgical precision and real-time adjustments for optimal results.
- Adoption of non-surgical LAMS (Local Anesthetic Minimal-Invasive Liposuction) provides patients an effective and minimally invasive solution to water retention, minimizing downtime and discomfort.
- Comprehensive post-treatment care, including tailored diet and nutrition counseling, supports long-term management of swelling, fluid balance, and body composition.
- Dedicated programs, such as the Hourglass Hip service, allow for customized solutions to meet individual aesthetic and physical goals associated with water retention.
- Commitment to research, innovation, and education ensures patients benefit from the latest advancements and best-practice guidelines in the management of water retention and obesity.
- Extensive support services—including meal diary app monitoring, seminars, and educational resources—equip patients with tools for sustained improvement and relapse prevention.
In summary, 365mc Hospital delivers an all-encompassing, technologically advanced, and results-oriented approach to the treatment of water retention, making it the premier choice for patients seeking safe, effective, and lasting solutions in Korea.
You can check out their website here: 365mc Hospital Website
Three Wishes Clinic - Myeongdong
Three Wishes Clinic, located just steps from Myeongdong Station exit 9 in central Seoul, is a renowned destination for modern aesthetic and medical treatments, receiving consistently high praise from both local and international patients. The clinic prides itself on blending safety, professionalism, and the latest technological advances to deliver a highly satisfying patient experience. With a focus on minimally invasive procedures and tailored care, Three Wishes Clinic has established a strong reputation in the competitive field of Korean medical aesthetics.
Specializing in a diverse range of treatments, the clinic offers options for facial and body contouring, feminine wellness, advanced skin therapies, and semi-permanent makeup. From petite enhancements such as botox, fillers, and fat-dissolving injections to innovative treatments addressing water retention and body aesthetics, Three Wishes Clinic ensures each patient receives individualized solutions. The clinic’s comprehensive care extends to rejuvenating procedures like Shurink, CO2 laser, PDT acne therapy, and various skin care treatments, all designed to help clients look and feel their best with effective, safe, and cutting-edge methods.
You can check out their website here: Three Wishes Clinic - Myeongdong Website
365mc Hospital - Sinsa
365mc Hospital - Sinsa is widely regarded as the best clinic in Korea for addressing water retention and related physical concerns due to its specialized expertise in advanced body contouring and liposuction procedures. The hospital’s expert team employs the latest technology and minimally invasive methods, such as LAMS (Liposuction Assisted Morphological Surgery), to deliver precise and highly effective results with minimal downtime for patients. With a comprehensive approach that includes targeted liposuction for the abdomen, arms, thighs, love handles, and face, 365mc ensures that each client receives a personalized treatment plan aimed at reducing localized fat deposits that can contribute to the discomfort and appearance of water retention. Renowned for prioritizing safety, responsibility, and client satisfaction, 365mc Hospital - Sinsa stands out as a leader in obesity and water retention treatment, making it the top choice for those seeking cutting-edge, medically supervised care in Korea.
You can check out their website here: 365mc Hospital - Sinsa Website
Seeking "Diet IV Therapy" and "Diet Pills" in South Korea: A Medical Tourist's Guide
South Korea is a top destination for medical tourism, known for high-quality care, advanced technology, and experienced doctors—especially in cosmetic and reconstructive surgery. The healthcare system is efficient and often less expensive than in the US or Europe, with major hubs in Seoul, Busan, Daegu, and Jeju Island.
The Process in South Korea for Medical Tourists
If you’re considering "Diet IV therapy" or "Diet Pills" in South Korea, here’s what to expect:
- Eligibility and Medical Considerations: For diet pills, you’ll need a BMI of 30+ (or 27+ with health issues). Both IV therapy and diet pills require a full medical history and medication list to check for risks. Some clinics may not strictly follow these guidelines, so be cautious.
- Initial Consultation and Assessment: You’ll start with a thorough evaluation at a hospital or weight loss clinic, including a physical exam, medical history, and discussion of goals. Bringing records from your home doctor can help.
- Prescription and Dispensing (for Diet Pills): If eligible, you’ll get a prescription for medications like Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, or Saxenda, which are available in major cities.
- Medication Acquisition and Regulations: Prescriptions are filled at local pharmacies. South Korea has strict drug import rules—narcotics (including CBD oil) are banned, and non-narcotics are allowed only in limited amounts with documentation.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-ups are essential for monitoring progress and side effects. Some clinics offer packages that include tests and post-treatment care. Medical tourism agencies can help with logistics and interpretation.
Cost Comparison: South Korea vs. Other Countries (from a Medical Tourist's Perspective)
South Korea offers competitive prices, but costs vary widely, especially for "Diet IV therapy." "Beauty" or "anti-aging" drips are much pricier than basic nutrient drips, often reflecting branding rather than medical necessity.
Table 4: Comparative Costs of Diet IV Therapy (per session)
| Procedure | South Korea (USD) | USA (USD) | Mexico (USD) | Turkey (USD) | Thailand (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diet IV Therapy (session) | $100 - $200 (nutrient drips $18-$45; beauty/anti-aging $150-$700+) | ~$299 | $440 - $470 | $150 - $250 | ~$50 |
Prescription weight loss medications are also generally less expensive in South Korea.
Table 5: Comparative Costs of Prescription Weight Loss Medications (1-month supply)
| Medication | South Korea (USD) | USA (USD) | Mexico (USD) | Turkey (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wegovy (Semaglutide) | $271 - $550 | ~$1,350 | N/A | N/A |
| Ozempic (Semaglutide) | $800 - $1,000 | ~$1,000 | $750 - $1,000 | N/A |
| Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) | ~$1,023 | ~$1,000 | N/A | N/A |
| Saxenda (Liraglutide) | ~$1,349 | N/A | ~$100 | N/A |
Don’t forget about hidden costs—consultations, follow-ups, hospital stays, travel, and interpreter services can add up quickly.
Table 6: Additional Costs for Medical Tourists in South Korea
| Cost Item | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Consultation Fees | $200–$500 (may be discounted/complimentary via agencies) |
| Follow-up Visits | $100–$300 |
| Hospital Stays (per night) | $100–$300 |
| Additional Medications | $50–$150 (post-op meds often included) |
| Travel and Accommodation | $1,000–$2,000+ (depends on stay) |
| Interpreter Services | $182 (half-day), $218 (full-day) |
| Upfront Deposit | ~10% of procedure cost |
Patient Experiences and Effectiveness: What the Data Shows
Experiences with "Diet IV Therapy" for Swelling and Related Concerns
Many people report feeling great after IV drips—energized, refreshed, or relaxed. Some use them for hangovers, dehydration, or stress. In South Korea, office workers and students use nutrient drips to fight fatigue, sometimes noticing better skin or more energy.
However, scientific evidence doesn’t support these claims. Major medical organizations don’t recommend IV therapy for weight loss or general wellness. Studies show that even saline-only IVs can produce a placebo effect. For water retention, IV therapy isn’t proven to help and can actually make things worse by causing overhydration.
Experiences with "Diet Pills" for Weight Management and Swelling
Diet pills come with a high rate of side effects. A KFDA survey found that 70% of users experienced issues like dizziness, thirst, nausea, and depression. Other side effects include gastrointestinal problems, gallbladder disease, and psychological symptoms. Many people regain weight after stopping the pills.
Regulators have warned about risks from ingredients like sibutramine and orlistat, which can cause heart or liver problems. Diet pills are not a direct solution for water retention and can sometimes even cause edema. Using them for swelling is not recommended and can be dangerous.
Recommendations for Patients: Making Informed Health Decisions
If you’re dealing with "water retention" or a "swollen body," here’s what you should do:
- Always Consult a Healthcare Professional: Swelling can signal serious conditions like heart, kidney, or liver disease, blood clots, preeclampsia, or malnutrition. Self-treating can delay needed care and lead to complications.
- Use Evidence-Based Treatments: Managing water retention means treating the underlying cause—this could involve diuretics, dialysis, or specific care for heart, kidney, or liver issues. For malnutrition-related edema, careful medical supervision is key.
- Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Habits: For mild cases or as part of treatment, focus on:
- Balanced Diet: Cut back on sodium, eat more fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Adequate Hydration: Drink enough water to support kidney function.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for 150–300 minutes of moderate cardio and 75–150 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
- Good Sleep and Stress Management: These help regulate fluid balance and hormones.
- Be Cautious with Medical Tourism: If seeking treatment abroad:
- Verify Medical Necessity: Make sure the treatment is appropriate for your condition.
- Research Clinics: Check credentials and accreditations.
- Budget Carefully: Include all costs, not just the procedure.
- Know the Laws: Follow drug import rules to avoid legal trouble.
Key Takeaways for Your Health Journey
- "Post-vacation weight" is often just temporary water retention—give your body time to adjust.
- "Diet IV therapy" is for severe deficiencies or when oral absorption isn’t possible—not for general wellness, weight loss, or water retention. Its broader benefits aren’t proven and it carries real risks.
- "Diet pills" are strong medications for obesity, not a quick fix for weight loss or swelling. They have significant side effects and should only be used under strict medical supervision.
- The best way to manage water retention is through accurate diagnosis, treating the underlying cause, and making sustainable lifestyle changes.
References
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24