Medical Tourism Blog
Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea | Best Clinics, Costs, Procedure Types & More

Table of contents
- What Is Stem Cell Disease Therapy?
- Best Stem Cell Disease Therapy Clinics in Korea
- Getting Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea
- Cost of Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea
- Alternatives to Stem Cell Disease Therapy
- Conclusion
Could the future of medicine lie in the ability to regenerate our own tissues and organs? Stem cell disease therapy is revolutionizing the field of regenerative medicine, presenting groundbreaking possibilities for treating conditions once deemed incurable. This article explores why South Korea is leading the charge in this innovative treatment path, offering insights into the best clinics, cost considerations, and alternatives for those seeking cutting-edge medical solutions.

What Is Stem Cell Disease Therapy?
Stem Cell Disease Therapy, often referred to as regenerative medicine, is a groundbreaking medical procedure that leverages the unique capabilities of stem cells to treat or even cure a wide range of diseases and disorders. Unlike traditional therapies that typically focus on treating symptoms or halting the progression of a disease, stem cell therapy aims to repair or replace damaged cells, tissues, and organs.
The Science Behind Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are a special type of cell capable of developing into different cell types in the body. They can divide and renew themselves over long periods and have the potential to repair tissues by differentiating into specialized cells. There are primarily two types of stem cells used in therapies:
-
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These are derived from early-stage embryos and have the ability to turn into any cell type in the body, making them highly versatile for therapeutic use.
-
Adult Stem Cells (ASCs): Also known as somatic stem cells, these are found in various tissues like the bone marrow, blood, and fat. They are more specialized than ESCs but are crucial for more targeted therapies, such as hematopoietic stem cells for blood-related disorders.
Procedure Steps
The process of Stem Cell Disease Therapy typically involves several stages:
-
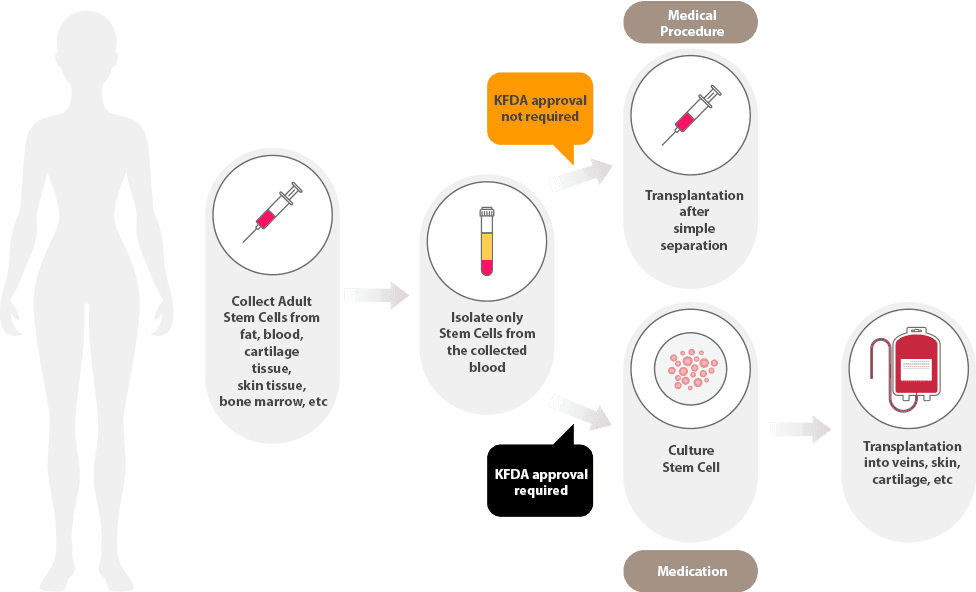
Collection: The first step is to harvest stem cells either from the patient's own body (autologous) or from a donor (allogeneic). Methods of collection vary; for instance, bone marrow extraction or liposuction may be used.
-
Processing: The collected stem cells are then isolated, purified, and sometimes expanded in a lab setting. This step ensures that a sufficient number of healthy, functional stem cells are available for transplantation.
-
Conditioning: Before the actual transplant, patients may undergo conditioning regimens such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This is particularly common in cases involving blood or immune disorders, to prepare the body to accept and integrate the new stem cells.
-
Transplantation: The processed stem cells are introduced into the patient’s body through an intravenous (IV) infusion. The procedure is minimally invasive and pain-free, similar to a blood transfusion.
-
Engraftment and Monitoring: After the infusion, the stem cells start to migrate to the target site, where they grow and differentiate into the needed cell types. Continuous monitoring ensures that the new stem cells are engrafting properly and that there are no adverse reactions.
Applications and Benefits
Stem Cell Disease Therapy has a wide range of applications, from treating blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma to repairing heart tissue damaged by myocardial infarction. It also shows promise in treating neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as for various genetic disorders and orthopedic injuries.
The benefits of stem cell therapy are manifold, including reduced recovery times, fewer surgical complications, and the potential for lasting cures rather than temporary relief. Additionally, since autologous stem cells are derived from the patient’s own body, the risk of immune rejection is significantly minimized.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its promise, Stem Cell Disease Therapy is not without challenges. Ethical concerns primarily arise from the use of embryonic stem cells, leading to rigorous regulations and necessitating ethical sourcing. Moreover, the high cost and technical complexity make the therapy less accessible for widespread use. Research is ongoing to better understand and overcome these challenges, making the future of stem cell therapy continually evolving and increasingly promising.
Who is Stem Cell Disease Therapy for?
- Individuals with Blood Cancers:
- Patients with leukemia, multiple myeloma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma often benefit from stem cell transplants following intensive chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Patients with Blood Disorders:
- Conditions such as sickle cell anemia can be treated with stem cell therapies.
- People with Broken Bones:
- Stem cells from donated tissue combined with other materials can help in treating and repairing broken bones.
- Individuals Affected by Disorders of the Bone Marrow:
- Those suffering from aplastic anemia can benefit from stem cell therapies as these conditions damage the blood-forming stem cells in the bone marrow.
- Patients with Myeloproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas:
- Stem cell treatments can be significant for patients dealing with these disorders where the normal production of blood cells is affected.
- Recipients of Cord Blood Treatments:
- Stem cells from donated cord blood, approved by the U.S. FDA, can treat various blood disorders effectively.
- Medical Research Subjects:
- Researchers use stem cells to understand disease mechanisms, test new treatments, and explore potential cures, making patients who participate in clinical trials indirect beneficiaries.
This broad spectrum of beneficiaries underlines the versatile and critical application of stem cell therapies in treating and managing various severe health conditions.
Best Stem Cell Disease Therapy Clinics in Korea
Listed below are the best clinics in Korea:
| Clinic Name | Key Features | Special Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Cellinique Clinic | Premier destination for stem-cell-disease-therapy, luxurious recovery rooms, highly skilled medical professionals | Re-cell Program, SVF (Stromal Vascular Fraction) intravenous injection |
| SH Clinic | Advanced stem cell disease therapy, comprehensive women's and men's health services, personalized care | Stem cell harvesting and culturing, targeted tissue regeneration |
| Lydian Plastic Surgery Clinic | Renowned for advanced stem cell treatments, expert guidance by Dr. An Kyung Chun, holistic approach to rejuvenation | Precise stem cell collection, targeted injections, minimally invasive techniques |
Cellinique Clinic
Cellinique Clinic stands out as the premier destination for stem-cell-disease-therapy in Korea, thanks to its groundbreaking Re-cell Program: Premium Whole Body Care. This innovative program integrates the rejuvenative power of stem cells with supplementary procedures to enhance both health and beauty, allowing individuals to lead vibrant lives by optimizing bodily functions and skin health. At the heart of the Re-cell Program is the SVF (Stromal Vascular Fraction) intravenous injection, which involves extracting autologous adipose-derived stem cells and administering them intravenously. This procedure offers comprehensive anti-aging benefits, targeting specific areas for care, and providing whole-body rejuvenation by revitalizing the body at a cellular level. The clinic's state-of-the-art facility in Gangnam is staffed by a team of highly skilled medical professionals and features luxurious recovery rooms akin to hotel accommodations. With a focus on both physical and aesthetic harmony, Cellinique Clinic combines cutting-edge procedures to support overall health, improve skin health, alleviate pain, and enhance mobility, making it the best choice for those seeking advanced stem cell therapies in Korea.
You can check out their website here: Cellinique Clinic Website
SH Clinic
SH Clinic, located in the vibrant district of Sinsa, Korea, is a premier medical facility offering a wide array of specialized healthcare services. Among its diverse offerings, the clinic is renowned for its advanced stem cell disease therapy, a cutting-edge treatment that utilizes the regenerative capabilities of stem cells to repair and rejuvenate damaged tissues. This innovative therapy is designed to improve metabolic functions and enhance overall health, making it a sought-after option for patients seeking holistic health improvements. The clinic's approach involves harvesting stem cells from the patient's own body, culturing them to increase their potency, and then injecting them into targeted areas to stimulate tissue regeneration and repair. This process not only addresses a variety of health issues but also promotes a stronger immune system and supports weight management.
In addition to its stem cell therapy, SH Clinic offers comprehensive women's health services, including treatments for incontinence, vaginal dryness, and safe abortion services. The clinic also provides specialized male urology procedures, couple’s therapy, and sexual health treatments aimed at enhancing intimacy and satisfaction for midlife couples. With a focus on personalized care, SH Clinic ensures that each patient receives tailored treatment plans to meet their individual health goals. The clinic's commitment to state-of-the-art treatments and comprehensive follow-up care makes it a leader in the field of regenerative medicine and holistic health solutions. Whether seeking to improve skin texture, support brain health, or manage weight, patients can experience transformative health benefits at SH Clinic.
You can check out their website here: SH Clinic Website
Lydian Plastic Surgery Clinic
Lydian Plastic Surgery Clinic in Korea stands out as the premier destination for stem cell disease therapy, offering a unique blend of cutting-edge medical innovation and personalized care. Situated in the prestigious Cheongdam area of Gangnam, Seoul, the clinic is renowned for its advanced stem cell treatments that harness the regenerative power of the patient's own cells to repair and rejuvenate damaged tissues, enhance metabolic functions, and boost overall health. Under the expert guidance of Dr. An Kyung Chun, a globally recognized specialist with over two decades of experience, Lydian Clinic provides a comprehensive approach to health and wellness. The clinic's stem cell therapy process involves a meticulous consultation, precise stem cell collection, and targeted injections, ensuring optimal results for conditions such as skin texture improvement, brain health support, weight management, and immune system enhancement. With a commitment to excellence and a focus on minimally invasive techniques, Lydian Clinic not only promises transformative health benefits but also offers a holistic approach to rejuvenation, making it the best choice for those seeking stem cell disease therapy in Korea.
You can check out their website here: Lydian Plastic Surgery Clinic Website
Getting Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea
Stem cell disease therapy is a promising treatment modality that leverages the body's own regenerative capabilities to repair and replace damaged tissues. South Korea is at the forefront of this innovative medical practice, thanks to its advanced technology and robust healthcare infrastructure. Here, we will demystify the procedure of getting stem cell disease therapy in Korea.
Initial Consultation and Diagnosis
The process begins with an initial consultation and a thorough diagnostic evaluation. Patients consult with healthcare providers who specialize in stem cell therapy to assess their medical history, current health status, and suitability for the treatment. Diagnostics often include blood tests, imaging studies (like MRI or CT scans), and other specialized tests to understand the extent and nature of the disease or injury.
Personalized Treatment Plan
Once the patient is deemed suitable for stem cell therapy, a personalized treatment plan is developed. This plan outlines the type of stem cells to be used, the source of these cells, and the implantation method. Typically, stem cells can be derived from autologous sources (the patient's own body) or allogeneic sources (donor cells).
Stem Cell Harvesting
If autologous stem cells are to be used, the next step involves harvesting these cells from the patient. Common sources include bone marrow and adipose (fat) tissue. The extraction procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia, using minimally invasive techniques. Bone marrow is usually extracted from the pelvic bone, while adipose tissue is harvested via liposuction.
Stem Cell Processing
Once harvested, the collected cells are taken to a laboratory for processing. Here, the stem cells are isolated, purified, and expanded under stringent sterile conditions. This process may take several hours to a few days, depending on the volume of cells required. Sophisticated bioreactors and culture systems are often utilized to ensure the cells’ viability and potency.
Stem Cell Administration
The administration of stem cells is a critical phase of the therapy. Depending on the condition being treated, stem cells may be injected directly into the affected area (such as joints for osteoarthritis), infused into the bloodstream, or delivered systemically. This procedure is usually performed in a clinical setting, and may require imaging guidance (like ultrasound or fluoroscopy) to ensure precise placement.
Post-Treatment Care
After the treatment, patients typically undergo a period of observation to monitor for any immediate adverse reactions. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to track the patient's progress and analyze the therapeutic outcomes. Additional supportive therapies, such as physical rehabilitation, may be recommended to optimize recovery.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Considerations
Korea’s stringent regulatory framework ensures that stem cell therapies are conducted ethically and safely. The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) monitors and regulates the development, production, and clinical application of stem cell products. Clinics and hospitals must adhere to rigorous standards to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Success Rates and Patient Outcomes
While individual results can vary, numerous clinical trials and patient testimonials underscore the potential efficacy of stem cell therapy for various conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and orthopedic injuries. Patients often report improvements in function, pain relief, and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea is a comprehensive process that involves meticulous planning, cutting-edge technology, and rigorous regulatory standards to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Cost of Stem Cell Disease Therapy in Korea
When considering the cost of Stem Cell Disease Therapy, it's evident that the financial burden can vary significantly depending on the country in which the treatment takes place. South Korea has emerged as a prominent destination for medical tourism, particularly in the field of stem cell research and therapy, largely due to its relatively competitive pricing and high-quality healthcare services.
In South Korea, the cost of Stem Cell Disease Therapy typically ranges from $20,000 to $50,000. This includes the cost of initial consultation, stem cell harvesting, laboratory procedures, and follow-up treatments. The relatively lower cost is attributed to advanced healthcare infrastructure, cutting-edge technology, and government support for medical research and innovation.
In comparison, the United States remains one of the most expensive countries for stem cell therapies. Patients seeking treatment in the U.S. often face prices ranging from $30,000 to $100,000 depending on the complexity of the condition, the type of stem cells used, and the specific protocol of the treatment center. The high cost can be attributed to stringent regulatory requirements, extensive clinical trials, and higher operational costs.
Europe presents a mixed landscape in terms of pricing for stem cell therapies. Countries like Germany and Switzerland offer high-quality treatments but at a premium price, often in the range of $40,000 to $90,000. On the other hand, nations such as Poland and Hungary might offer similar treatments for a lower cost, between $20,000 and $40,000, due to differences in operational costs and healthcare subsidies.
Across Asia, besides South Korea, countries such as Japan, Thailand, and India also offer competitive pricing. Japan, a pioneer in regenerative medicine, offers treatments typically ranging from $25,000 to $60,000. Thailand and India, known for their burgeoning medical tourism industry, provide even more cost-effective solutions, usually within the $10,000 to $30,000 range, making them attractive options for patients seeking more affordable treatments without compromising on quality.
In summary, South Korea stands out as a cost-effective yet high-quality option for Stem Cell Disease Therapy when compared to countries like the USA, various European nations, and even other Asian countries. With continued advancements and government support, Korea holds a promising position in the global landscape of medical innovation.
Alternatives to Stem Cell Disease Therapy
1. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a groundbreaking treatment strategy that leverages the body's immune system to combat diseases, particularly cancer. It involves the use of substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function. Common forms of immunotherapy include monoclonal antibodies, checkpoint inhibitors, and cancer vaccines.
How It Works: Immunotherapy aims to enhance the immune system's natural defenses. Monoclonal antibodies, for instance, are designed to target specific antigens on the surface of cancer cells, marking them for destruction by immune cells. Checkpoint inhibitors release the "brakes" on the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells more effectively.
Advantages: This treatment can be tailored to individual patients, potentially leading to fewer side effects than traditional treatments like chemotherapy. It also offers hope for cancers that do not respond well to other treatments.
2. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is an innovative medical treatment that involves altering a patient's genes to treat or prevent disease. It works by repairing, reprogramming, or replacing faulty genes within an individual's cells.
How It Works: There are several techniques in gene therapy, including gene transfer, which introduces a new or modified gene into a patient's cells, and gene editing, which directly modifies DNA to correct genetic disorders. The most notable tool for gene editing is CRISPR-Cas9, which allows precise modifications to the genome.
Advantages: Gene therapy holds the potential for treating a wide range of diseases, from single-gene disorders like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy to complex conditions like cancer and HIV. Its ability to address the root cause of genetic disorders rather than just managing symptoms offers a promising avenue for long-term cures.
3. Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine focuses on regenerating, repairing, or replacing damaged tissues and organs through various methods, including cell therapy, tissue engineering, and the use of biologically active molecules.
How It Works: This field encompasses a variety of techniques such as the use of scaffold materials to encourage cellular growth, and the application of growth factors to stimulate tissue repair. Advances in 3D printing have also enabled the creation of complex tissue structures from biomaterials and living cells.
Advantages: Regenerative medicine aims to restore normal function by healing tissues that have been damaged by age, disease, or injury. It offers the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for patients with chronic conditions and may reduce the need for organ transplants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Korea's advancements in stem cell disease therapy stand at the forefront of medical innovation, offering a beacon of hope for patients worldwide. With robust government support, cutting-edge research, and a collaborative ecosystem involving academia and industry, Korea is not only making significant strides in treating previously intractable conditions but is also setting a global benchmark for the future of regenerative medicine. As these therapies continue to evolve, they promise substantial improvements in patient outcomes and potential cures, positioning Korea as a key player in the transformative landscape of global healthcare.